Young Adults Likely Produce Toxic Spike Protein for Over a Year After COVID mRNA Injection
How many more studies like this until they admit the truth?
This article originally appeared on Focal Points and was republished with permission.
Guest post by Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
Persistent elevation of inflammatory cytokines over one year post-injection indicates ongoing immune stimulation likely driven by systemic Spike protein production.
The study titled, Altered Circulating Cytokine Profile Among mRNA‐Vaccinated Young Adults: A Year‐Long Follow‐Up Study, was just published in the journal Immunity, Inflammation and Disease:
Objectives
This longitudinal study aimed to assess the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on cytokine profile.
Methods
A total of 84 Saudi subjects (57.1% females) with mean age of 27.2 ± 12.3 participated in this longitudinal study. Anthropometric data and fasting blood samples were obtained at baseline and after final vaccination, with an average follow-up duration of 14.1 ± 3.6 months for adolescents and 13.3 ± 3.0 months for adults, calculated from the first dose of vaccination. Assessment of cytokine profiles was done using commercially available assays.
Results
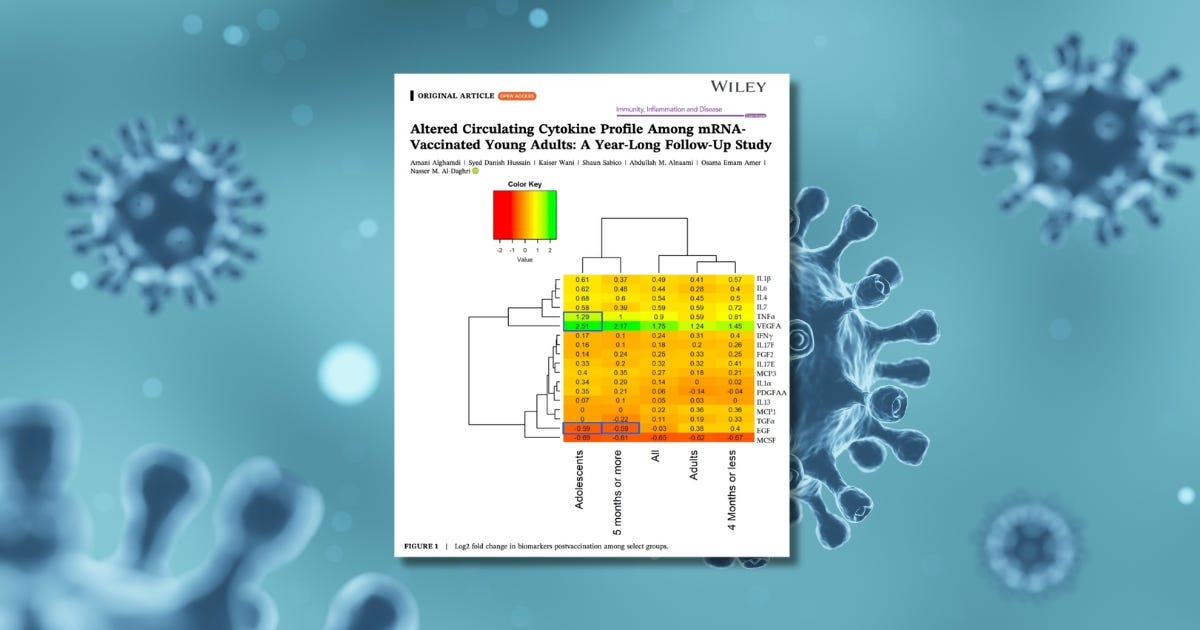
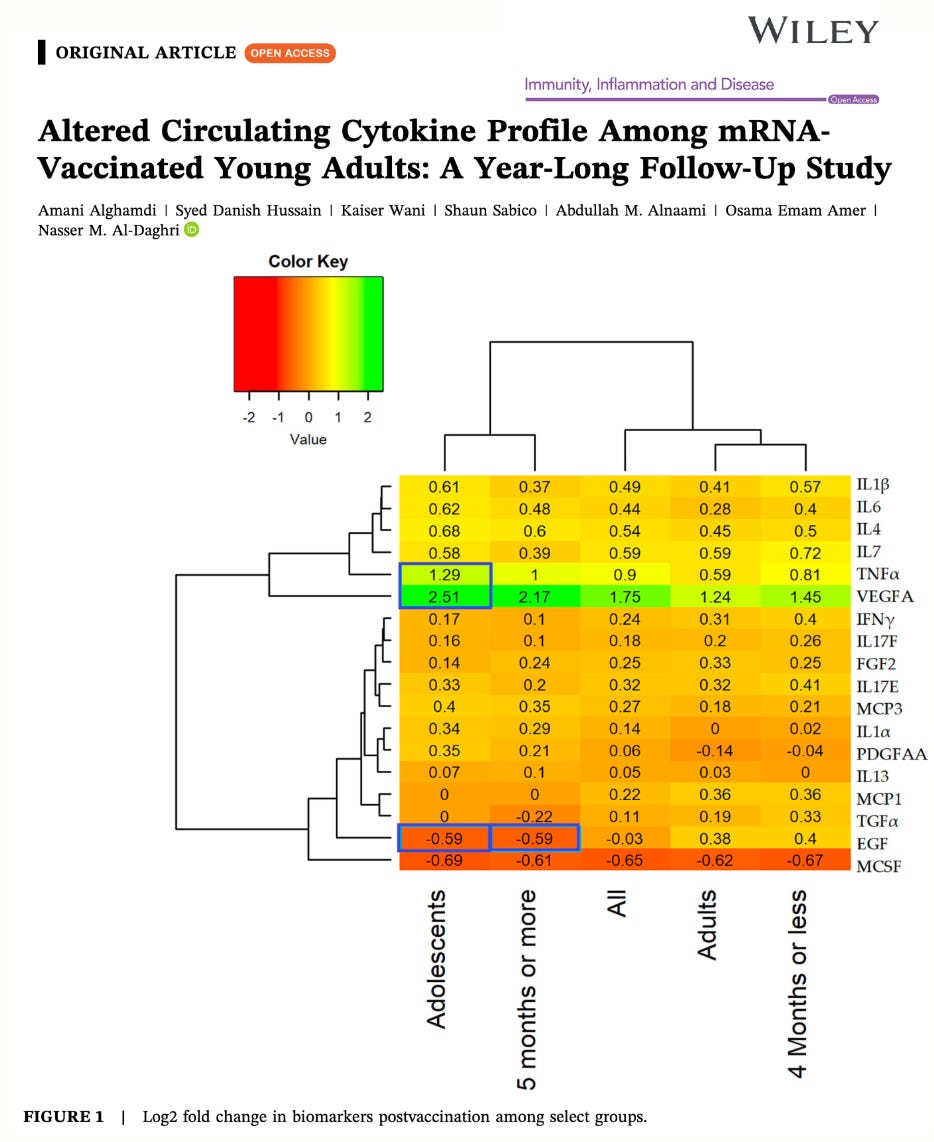
After follow-up, a significant increase in weight and body mass index was observed overall (p = 0.003 and p = 0.002, respectively). Postvaccination, significant increases were observed in several cytokines, including basic fibroblast growth factor 2 (p < 0.001), interferon gamma (IFNγ) (p = 0.005), interleukin-1 beta (IL1β) (p < 0.001), IL4 (p < 0.001), IL6 (p = 0.003), IL7 (p = 0.001), IL17E (p < 0.001), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1) (p = 0.03), MCP3 (p = 0.001), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) (p < 0.001), and VEGFA (p < 0.001). A significant reduction was observed only in macrophage colony-stimulating factor (p < 0.001). When adjusted for age, epidermal growth factor (EGF), IL4, IL6, MCP3, TNFα, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) remained statistically significant. Gender-based analysis revealed that men experienced greater increases in IL6 (p = 0.008), IL4 (p = 0.04), and TNFα (p = 0.015) compared to women. Age-based analysis showed that older participants had more pronounced increases in EGF (p = 0.011), IL6 (p = 0.029), MCP1 (p = 0.042), and TNFα (p = 0.017), while younger participants had a greater increase in VEGFA (p = 0.025).
Conclusions
The findings of this study indicated that COVID-19 vaccination resulted in an increase in cytokine levels, which signifies the persistence of the humoral immune response to messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines. This effect may be attributed to the persistent production of spike protein and highly inflammatory nature of mRNA–lipid nanoparticle. Additionally, the results suggested differences in cytokine levels based on gender and age. Notably, the cytokine profile remains favorably altered in young adults who received mRNA vaccinations, even after 1 year.
In other words, this study found that in young adults (mean age = 27.2), mRNA injection likely leads to sustained Spike protein production lasting at least one year—evidenced by persistently elevated levels of multiple proinflammatory cytokines. Elevation of inflammatory markers is likely to play a role in symptomatic long pandemic syndromes.
Key Points from the Study:
Long-Term Immune Stimulation
Participants showed significantly elevated cytokine levels 13–14 months post-vaccination, well beyond the expected duration of a typical immune response.
Cytokines Upregulated After mRNA Injection
TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-4, IL-7, IL-17E
These cytokines are associated with chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation, and autoimmune activation.
VEGFA (angiogenesis), FGF2, IFN-γ
These markers are linked to vascular remodeling, tissue repair, and persistent immune activation.
MCP-1, MCP-3
These markers are associated with chronic inflammation, vascular remodeling, and autoimmunity.
Only One Cytokine Decreased
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF) levels dropped significantly, possibly indicating immune system dysregulation.
Mechanistic Implication
The authors suggest this sustained cytokine activity may stem from the persistent expression of Spike protein, driven by:
Modified nucleoside-stabilized mRNA
Pro-inflammatory lipid nanoparticles known for systemic biodistribution
Biological and Clinical Concerns
Prolonged IL-6 and TNF-α elevation is linked to autoimmune conditions and post-acute inflammatory syndromes.
Persistent VEGFA suggests ongoing vascular endothelial activation and potential long-term cardiovascular effects.
These findings are not unexpected — 130 peer reviewed studies have documented:
I) the systemic biodistribution of the injected mRNA,
II) the persistence of both the synthetic mRNA and the spike protein it encodes, and
III) the toxic potential of the lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system used to transport the genetic payload.
As yet another study reveals grave harms linked to the COVID-19 mRNA injections, the case for their immediate removal from the market grows stronger and more urgent.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
www.mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Foundation and my personal account on X (formerly Twitter) for further content.
Copyright 2025 Focal Points